Dinosaur fossil News
The fossil is rare and around 80 million-year-old.
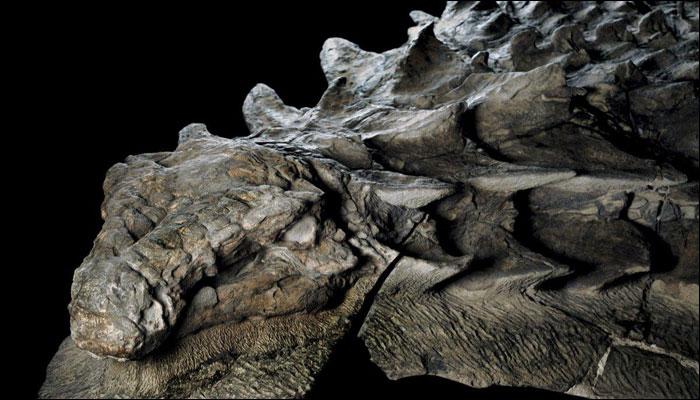
The fossil of the sauropod dinosaurs has tiny embryonic bones to patches of delicate fossilized skin, and even a skull and teeth of one of the creatures.
The new findings was led by Martin Kundrat of the Paleo BioImaging Lab at Pavol Jozef Šafárik University, in the Slovak Republic.
The creature has now been sent for analysis, including carbon dating, which will reveal its exact age.
The dinosaur was estimated to be about 100 million years old with its size believed to be the biggest ever found in Thailand
The rare skull was spotted at a construction site and experts say that it could help unlock numerous secrets about triceratops.
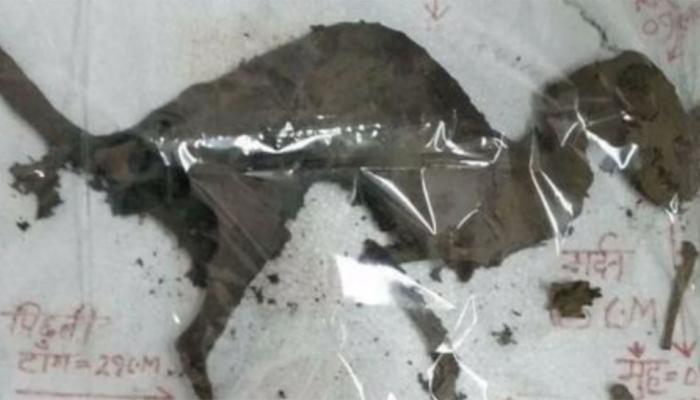
The remnants of skin which are fossilized, cover the armor plates on the dinosaur’s remains, which are petrified from the head to the hips.
In general, theropods, including Tyrannosaurus, are carnivorous. But Fukuivenator, which had a long neck, is believed to have been omnivorous.
The discovery of a 75-million-year-old dinosaur fossil in 2010 from Canada's Dinosaur Provincial Park in Alberta has now provided scientists an opportunity to fill in gaps in the evolution of other horned dinosaurs, such as Triceratops.
Ceratopsia was a group of plant-eating horned dinosaurs and the fossil studied by Longrich comes from a smaller cousin of the better known Triceratops, the leptoceratopsids.
The fossil, previously known at Bathygnathus borealis, was collected in 1845, and was named Bathygnathus borealis by palaeontologist Joseph Leidy.
Although the preserved feathers are extremely crushed due to sediment compaction, scanning electron microscopy shows a three-dimensional keratin structure to the feathers on the tail and body.
Loading...



)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
